Cloud Migration
WHAT IS CLOUD MIGRATION ?
Cloud migration is the process of moving data, applications or other business elements to a cloud computing environment. There are various types of cloud migrations an enterprise can perform. One common model is the transfer of data and applications from a local, on-premises data center to the public cloud. However, a cloud migration could also entail moving data and applications from one cloud platform or provider to another -- a model known as cloud-to-cloud migration. A third type of migration is to uncloud -- also known as a reverse cloud migration or declouding -- where data or applications are moved off of the cloud and back to a local data center.
BENEFITS OF CLOUD MIGRATION
The general goal or benefit of any cloud migration is to host applications and data in the most effective IT environment
possible, based on factors such as cost, performance and security.
For example, many organizations perform the migration of on-premises applications and data from their
local data center to public cloud infrastructure to take advantage of benefits, such as greater elasticity, self-service
provisioning, redundancy and a flexible, pay-per-use model.
CLOUD MIGRATION PROCESS
The steps or processes an enterprise follows during a cloud migration vary based on factors such as the type of
migration it wants to perform and the specific resources it wants to move. That said, common elements of a cloud
migration strategy include evaluating performance and security requirements, choosing a cloud provider, calculating
costs and making any necessary organizational changes.
Common challenges an enterprise faces during a cloud migration include interoperability, data and application
portability, data integrity and security, and business continuity. Without proper planning, a migration could negatively
affect workload performance and lead to higher IT costs -- thereby negating some of the main benefits of cloud
computing.
Depending on the details of the migration, an enterprise may choose to move an application to its new hosting
environment without any modifications -- a model sometimes referred to as a lift-and-shift migration. In other
cases, it might be more beneficial to make changes to an application's code or architecture before performing the
migration.
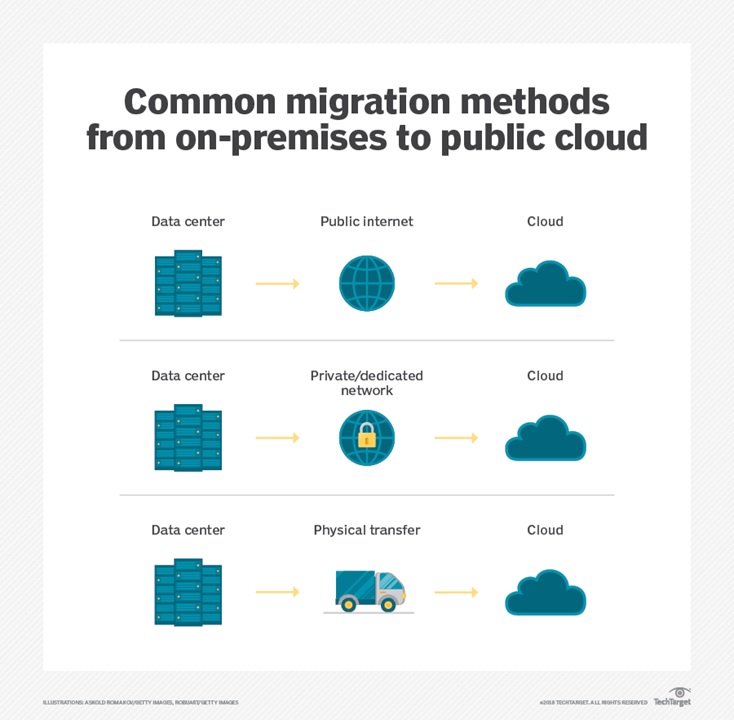
In terms of data transfers from its local data center to the public cloud, an enterprise also has several options. These
include the use of the public internet, a private/dedicated network connection or an offline transfer, in which an
organization uploads its local data onto an appliance and then physically ships that appliance to a public cloud
provider, which then uploads the data to the cloud. The type of data migration an enterprise chooses -- online or
offline -- depends on the amount and type of data it wants to move, as well as how fast it needs to complete the
migration.
CLOUD MIGRATION - TOOLS AND SERVICES
There are various tools and services available to help an enterprise plan and execute a cloud migration.
For example, public cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google, offer
cloud migration services to support private/dedicated networks for data transfers, as well offline migrations.
Public cloud providers also offer tools to help an enterprise plan and track the progress of a migration. These tools, for
example, might collect information about an enterprise's on-premises environment, such as system dependencies, to
help the company make a more informed migration plan.
Examples of migration services from public cloud providers include:
* AWS Migration Hub
* Azure Migrate
* Google Cloud Data Transfer Service
* AWS Snowball
* Azure Import/Export
* Google Transfer Appliance
TechNubem is a trading name of Payment Services Integrators Limited.
Copyright © Payment Services Integrators Ltd. All rights reserved worldwide. Company Registered in England and Wales. No. 08054142
